Windows Phone
Microsoft is giving up on its mobile OS aspirations for now. In Windows Phone, it produced a unique mobile OS; arguably the most original of the mobile OSes. Let's see how it got there.
The journey to Windows Phone 10 was a colourful one that spans three decades and includes many devices, and several different operating systems.
This story starts with the launch of Windows CE 1.0 in 1996.
Windows CE 1.0
Windows CE was launched in 1996 by Bill Gates, and laid the foundation for Microsoft's future mobile operating systems.
Referred to as Handheld PCs, the form factor of these devices was that of a small, portable PC, resembling more a tiny laptop than the mobile devices we're used to today.
But mobile they were, generally weighing less than 450 g. CPU speeds were in the 40-50 MHz range, and they usually came with monochrome screens with resolution of around 480×240 pixels.
Pocket Internet Explorer was also introduced with CE 1.0. It did not share a codebase with its desktop counterpart—instead it was written from scratch to be lightweight.
Device in class: HP 320LX

| Screen | Monochrome 640×240 |
| Input | 79 key keyboard Touchscreen Stylus |
| CPU | 40 MHz |
| RAM | 4 MB |
| ROM | 5 MB |
| Weight | 442 g |
Windows CE 2.0
Many regarded the first version of Windows CE to be a short-lived beta. With CE 2.0 Microsoft modularised the operating system, and expanded the number and types of device that could run it. Windows CE could now be used in diverse devices including cars, games consoles, and even kitchen utensils.
Supported architectures were ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, StrongARM, SuperH and x86.
Notably, Windows CE 2.0 added support for colour VGA screens, as well as built-in network support.
In all, there were 12 further updates to Windows CE 2.
Device in class: HP Jornada 820

| Screen | 256 colours 640×480 |
| Input | Keyboard Touchpad |
| CPU | Intel StrongARM 190 MHz |
| RAM | 16 MB |
| ROM | 16 MB |
| Weight | 1.1 kg |
| Size | 246×33×178 mm |
Pocket PC 2000
Based on Windows CE 3.0 which was launched in the same year, the only resolution supported by this release was 240×320 (QVGA).
Built-in apps included pocket versions of Microsoft's Office suite, including Pocket Word, Pocket Excel, and Pocket Outlook, as well as Notes, a note taking app with handwriting recognition.
The Pocket Internet Explorer browser saw improvements too, with features like Shrink-to-fit which resized web pages for small screens.
Infrared (IR) file beaming was also supported.
Device in class: Compaq iPAQ H3100
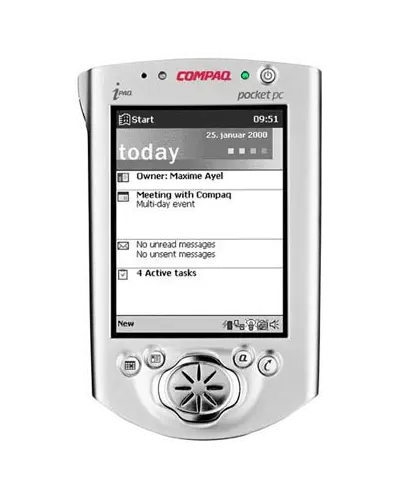
| Screen | Monochrome 240×320 |
| Input | Stylus Touchscreen D-pad Customisable buttons |
| CPU | Intel StrongARM 206 MHz |
| RAM | 16 MB |
| ROM | 16 MB |
| Weight | 163 g |
| Size | 5×3×6 mm |
Pocket PC 2002
This release mainly targeted Pocket PC devices, although a Phone Edition of the OS included cell phone functionality in addition to the PDA abilities.
Aesthetically, Pocket PC 2002 was designed to look like Windows XP.
WAP browsing support was added to Pocket Internet Explorer.
Device in class: Dell Axim X5

| Screen | Colour 240×320 |
| Input | Stylus Touchscreen D-pad Customisable buttons |
| CPU | Intel XScale 300 MHz |
| RAM | 32 MB |
| ROM | 32 MB |
| Weight | 196 g |
| Size | 5×3×6 mm |
Windows Mobile 2003
Windows Mobile 2003 came in a variety of editions, including Pocket PC Premium, Professional, Smartphone, and Pocket PC Phone.
It included a number of enterprise features such as VPN support, WiFi enhancements, and SMS APIs.
Device in class: O2 XDA II

| Screen | 16-bit colour 240×320 |
| Input | Touchscreen D-pad |
| CPU | Intel XScale 400 MHz |
| RAM | 128 MB |
| ROM | 64 MB |
| Weight | 190 g |
| Size | 5.117×3.28×6.2 mm |
Windows Mobile 5.0
Windows Mobile 5 was available in Pocket PC and Smartphone editions, the former including touchscreen and MS Office, and the latter without.
A new memory architecture was added for persistent storage: RAM was used for running programs, not for storage, so that no data would be lost under power failure.
Device in class: Palm Treo 750v
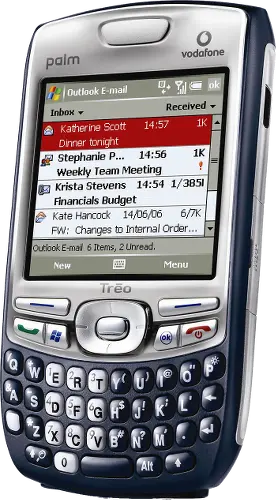
| Screen | 16-bit colour 240×240 |
| Input | Touchscreen Stylus D-pad Qwerty keyboard |
| CPU | Samsung 300 MHz |
| RAM | 100 MB |
| ROM | 60 MB |
| Weight | 154 g |
| Size | 111×58×22 mm |
Windows Mobile 6.0
Windows Mobile 6 introduced a new, simplified, naming scheme, with Classic, Standard, and Professional versions.
Professional ran on smartphones with touchscreens, Standard ran on mobile phones without touchscreens, and Classic which was for PDAs or Pocket PCs.
New screen sizes of 320×320 and 800×480 were supported.
Device in class: HTC Touch
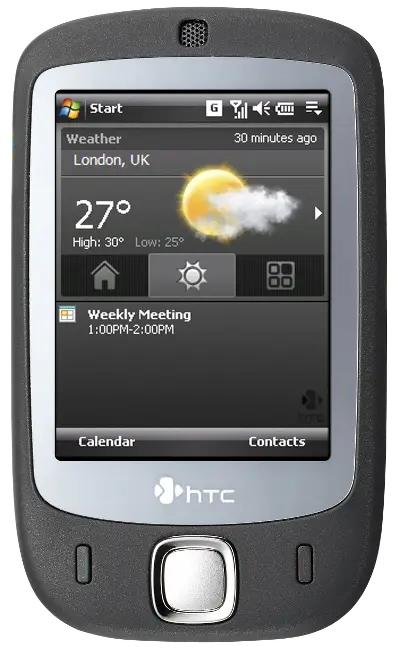
| Screen | 16-bit colour 240×320 |
| Input | Touchscreen Stylus D-pad |
| CPU | ARM 200 MHz |
| RAM | 128 MB |
| ROM | 256 MB |
| Weight | 112 g |
| Size | 100×58×14 |
Windows Mobile 6.1
Although this was a minor update to Windows Mobile 6.0 it included some key features and was well received.
It included a redesigned home screen, with a tile-based UI, and threaded SMS conversations.
Internet Explorer saw some improvements too, with full-page zooming.
Device in class: Sony Ericsson Xperia X1

| Screen | 16-bit colour 480×800 |
| Input | QWERTY keyboard Touchscreen Optical trackpad Stylus |
| CPU | ARM 11 528 MHz |
| RAM | 256 MB |
| ROM | 512 MB |
| Weight | 145 g |
| Size | 110×53×17 mm |
Windows Mobile 6.5
Windows Mobile 6.5 was a stopgap update to Windows Mobile 6.1 intended to bridge the gap between version 6.1 and the then-to-be-released Windows Mobile 7.
This release was significant in that it saw the OS become more finger-friendly. It featured a slick new Today screen with large, clean, expanding, text elements—parts of this UI would carry over into Windows Phone.
It also included a hexagonal tile-based Start Menu, which was innovative, but ultimately didn't stand the test of time.
Windows Marketplace for Mobile, an app store, was also launched with this release.
Device in class: Samsung Omnia Pro B7330

| Screen | 16-bit colour 320×320 |
| Input | QWERTY keyboard Touchscreen |
| CPU | ARM 11 528 MHz |
| RAM | 256 MB |
| ROM | 512 MB |
| Weight | 111 g |
| Size | 110×53×17 mm |
Windows Phone 7
Windows Phone 7 was the only version of Windows Phone based on Windows CE, as future versions moved to the Windows NT kernel.
Windows Phone 7 employed Microsoft's Metro UI, a design language focused on typography and simplified icons, as well as Live Tiles, a fresh, colourful, tile-based home screen, with fluid transitions between screens. It looked markedly different to its predecessors, and offered a unique alternative to Android and iOS.
Microsoft laid down minimum hardware specifications for Windows 7 handsets, which mandated 5 physical buttons, for Start, back, search, camera, and power., as well as CPU, GPU, screen, and connectivity requirements.
Device in class: HTC HD7

| Screen | 32-bit colour 480×800 |
| Input | QWERTY keyboard Touchscreen |
| CPU | Snapdragon S1 1.0 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 200 |
| RAM | 576 MB |
| ROM | 512 MB |
| Weight | 162 g |
| Size | 122×68×11 mm |
Windows Phone 8
Based on Windows NT kernel, and sharing Windows 8 code, Windows Phone 8 release saw a unification of Microsoft's mobile and desktop offerings, resulting in a more consistent experience for developers and users across platforms.
Resizable home screen tiles, 720p HD screens, Internet Explorer 10
Introduced in November 2011, the line is the result of a long-term partnership between Nokia and Microsoft—as such, most Lumia smartphones run the Windows Phone operating system, excluding some later models which run the newer Windows 10 Mobile. The Lumia name is derived from the partitive plural form of the Finnish word lumi, meaning "snow"
Device in class: Nokia Lumia 920
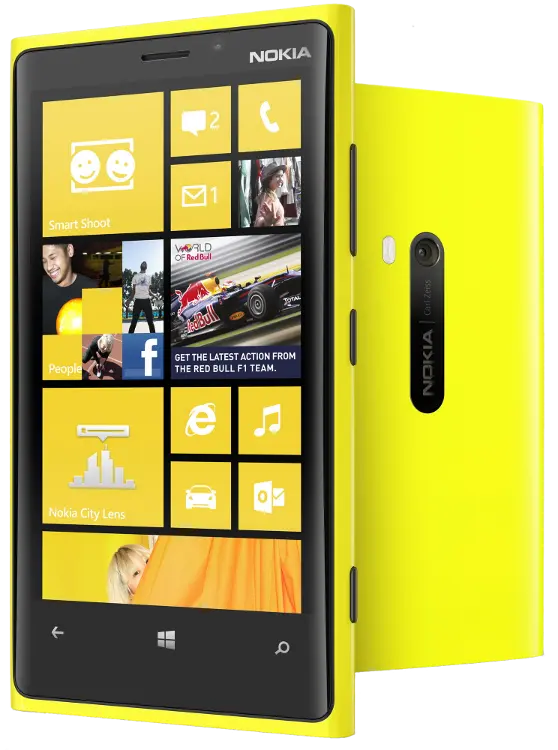

| Screen | 32-bit/16 M colours 1280×768 |
| Input | Touchscreen |
| CPU | Qualcomm Krait dual-core 1.5 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 320 |
| RAM | 1 GB |
| Weight | 185 g |
| Size | 130×71×11 mm |
Windows Phone 8.1
Windows Phone 8.1 saw significant upgrades to the Windows OS.
Cortana, Microsoft's voice activated digital assistant, came to the platform, and brought voice-based search to Windows Phone.
A new notifications panel, called Action Center, was also introduced which vastly improved notifications in Windows Phone
Internet Explorer 11
Device in class: HTC One M8

| Screen | 32-bit/16 M colours 1280×768 |
| Input | Touchscreen |
| CPU | Qualcomm Snapdragon 801 2.45 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 330 |
| RAM | 2 GB |
| Weight | 160 g |
| Size | 146×71×9 mm |
Windows 10 Mobile
This was the last iteration of the Windows Phone OS. It aimed to unify and provide greater consistency with its Windows 10 desktop counterpart.
It provided the new Universal Windows Platform (UWP) which allowed apps to be built for and run across all Windows 10 devices, whether desktop, mobile, or console.
Syncing was also improved between devices. For example, a notification dismissed on desktop would automatically be dismissed on mobile too.
Device in class: Microsoft Lumia 950 XL
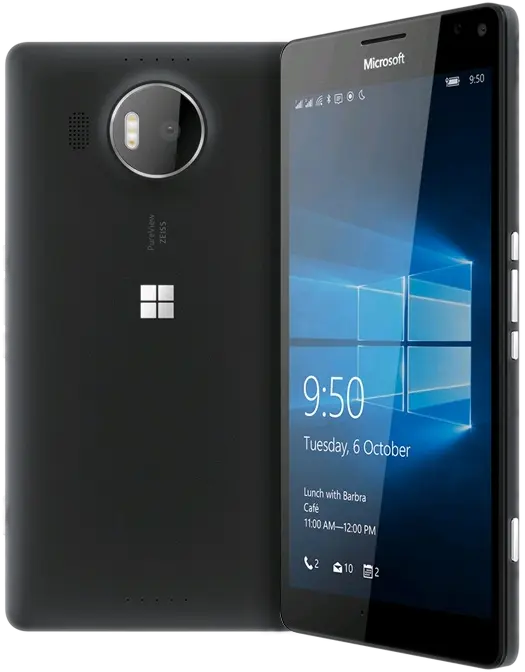

| Screen | 32-bit/16 M colours 1280×768 |
| Input | Touchscreen |
| CPU | 4×core Cortex A57 2GHz + 4×core Cortex A53 1.5 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 430 |
| RAM | 3 GB |
| Weight | 165 g |
| Size | 152×79×8 |
Windows Phone RIP
In October 2017 Microsoft's corporate vice president, Joe Belfiore, confirmed that, due to low market-share and lack of third-party development, Microsoft will no longer sell or manufacture new Windows 10 Mobile devices.
Existing devices will receive bug fixes and security updates only.
So long, Windows Phone. We will miss you.